no coLIRC – Linux Infrared Remote Control
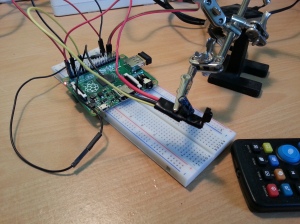
- Connect your IR receiver to your RPi. TSOP series are most recommended due to their satability (ex.
TSOP38238 IR receiver (ebay)– specification)
- Make sure you are connected to Internet: ‘ping google.com’ should produce answers from some IP address
- After connected to Internet, install ‘lirc’: sudo apt-get install lirc
- To enable lirc-rpi overlay (on that pin you connected) add the following line to config.txt (sudo nano /boot/config.txt):
dtoverlay=lirc-rpi,gpio_in_pin=18,gpio_out_pin=17
- reboot with for this new configuration to have effect
- After reboot, configure GPIO pin you just connected (assign gpio_out_pin to not connected one)
modprobe lirc-rpi gpio_in_pin-18 gpio_out_pin=17
- check the connection succeeded:
- ‘dmesg’ command should show the messages like below
- and you should have lirc0 device: ‘ls /dev/lirc0’
[ 4.791065] lirc_dev: IR Remote Control driver registered, major 246
[ 4.928351] lirc_rpi: module is from the staging directory, the quality is unknown, you have been warned.
...
[ 5.968099] lirc_rpi: auto-detected active low receiver on GPIO pin 18
[ 6.028343] lirc_rpi lirc_rpi: lirc_dev: driver lirc_rpi registered at minor = 0
[ 6.032275] lirc_rpi: driver registered!- kill the loaded lirc-rpi
‘ps aux | grep lirc’ – to know if lirc process exists
pi@(none) ~ $ ps aux | grep lirc
root 393 0.0 0.4 3644 1548 ? Ss 14:18 0:00 /usr/sbin/lircd --driver=default --device=/dev/lirc0
pi 3149 0.0 0.4 3556 1776 pts/0 S+ 14:20 0:00 grep --color=auto lirc
In case ‘lirc’ process is there, use one of the following commands to kill it:
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc stop
sudo pkill lircNote: Just using ‘kill -QUIT <PID>’ will not help as the process lirc changes its PID constantly
-
- start sensing key signals by
mode2 -d /dev/lirc0
Now if you press any button on your remote you is supposed to get a sequence on your screen that describes timing diagram of that specific signal
-
- Teach LIRC about specific buttons of your remote control.
– First, save for yoursef LIRC’s default key-names
irrecord --list-namespace > ~/lirc_keys.txt
– Then, provide key-presses to the ‘irrecord‘ command: follow the instructions provided by the command and use your ~/lirc_keys.txt when asked to give names for specific buttons.
# Stop lirc to free up /dev/lirc0
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc stop
# Create a new remote control configuration file (using /dev/lirc0) and save the output to ~/lircd.conf
irrecord -d /dev/lirc0 ~/lircd.conf
# Make a backup of the original lircd.conf file
sudo mv /etc/lirc/lircd.conf /etc/lirc/lircd_original.conf
# Copy over your new configuration file
sudo cp ~/lircd.conf /etc/lirc/lircd.conf
# Start up lirc again
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc start
– After you are done lircd.conf will look like below
# Please make this file available to others
# by sending it to <lirc@bartelmus.de>
#
# this config file was automatically generated
# using lirc-0.9.0-pre1(default) on Sat Jan 9 11:49:38 2016
#
# contributed by
#
# brand: ./lirc.conf
# model no. of remote control:
# devices being controlled by this remote:
#
begin remote
name ./lirc.conf
bits 8
flags SPACE_ENC|CONST_LENGTH
eps 30
aeps 100
one 272 1843
zero 272 786
ptrail 272
pre_data_bits 8
pre_data 0xE2
gap 50265
toggle_bit_mask 0x0
begin codes
KEY_A 0xC4
KEY_B 0x44
KEY_C 0x84
KEY_D 0x04
end codes
end remote
- Add lirc-pi to the configuration:
– change LIRC configuration (sudo nano /etc/lirc/hardware.conf) as following:
# /etc/lirc/hardware.conf
#
# Arguments which will be used when launching lircd
LIRCD_ARGS=""
#Don't start lircmd even if there seems to be a good config file
#START_LIRCMD=false
#Don't start irexec, even if a good config file seems to exist.
#START_IREXEC=false
#Try to load appropriate kernel modules
LOAD_MODULES=true
# Run "lircd --driver=help" for a list of supported drivers.
DRIVER="default"
# usually /dev/lirc0 is the correct setting for systems using udev
DEVICE="/dev/lirc0"
MODULES="lirc_rpi"
# Default configuration files for your hardware if any
LIRCD_CONF=""
LIRCMD_CONF=""
- To have you lirc starting at RPi boot add the following line to your /etc/rc.local (sudo nano /etc/rc.local):
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc start- To see how LIRC decodes the keys you configured use ‘irw’ command and then press the buttons your LIRC learned.
Example:
pi@(none) ~ $ irw
000000000000e2c4 00 KEY_A ./lirc.conf
000000000000e2c4 01 KEY_A ./lirc.conf
000000000000e2c4 02 KEY_A ./lirc.conf
000000000000e284 00 KEY_C ./lirc.conf
000000000000e284 01 KEY_C ./lirc.conf
000000000000e284 02 KEY_C ./lirc.conf
Useful Links:






Pingback: RPi: Stationary Recording/Playback Training Assistance System | My Hobby of 'Making'
Thanks, Pasha. We surely will use you experience in our courses. Our students will study Raspbery Pi programming a little later – in few months.
🙂 will be glad to become alligned with you guys for our mutual benefit